- Nettoyage dentaire
- Soins des caries
- Soins parodontaux
- Endodontie
- Extraction des dents de sagesse
- Imagerie 3D
- Empreintes numériques
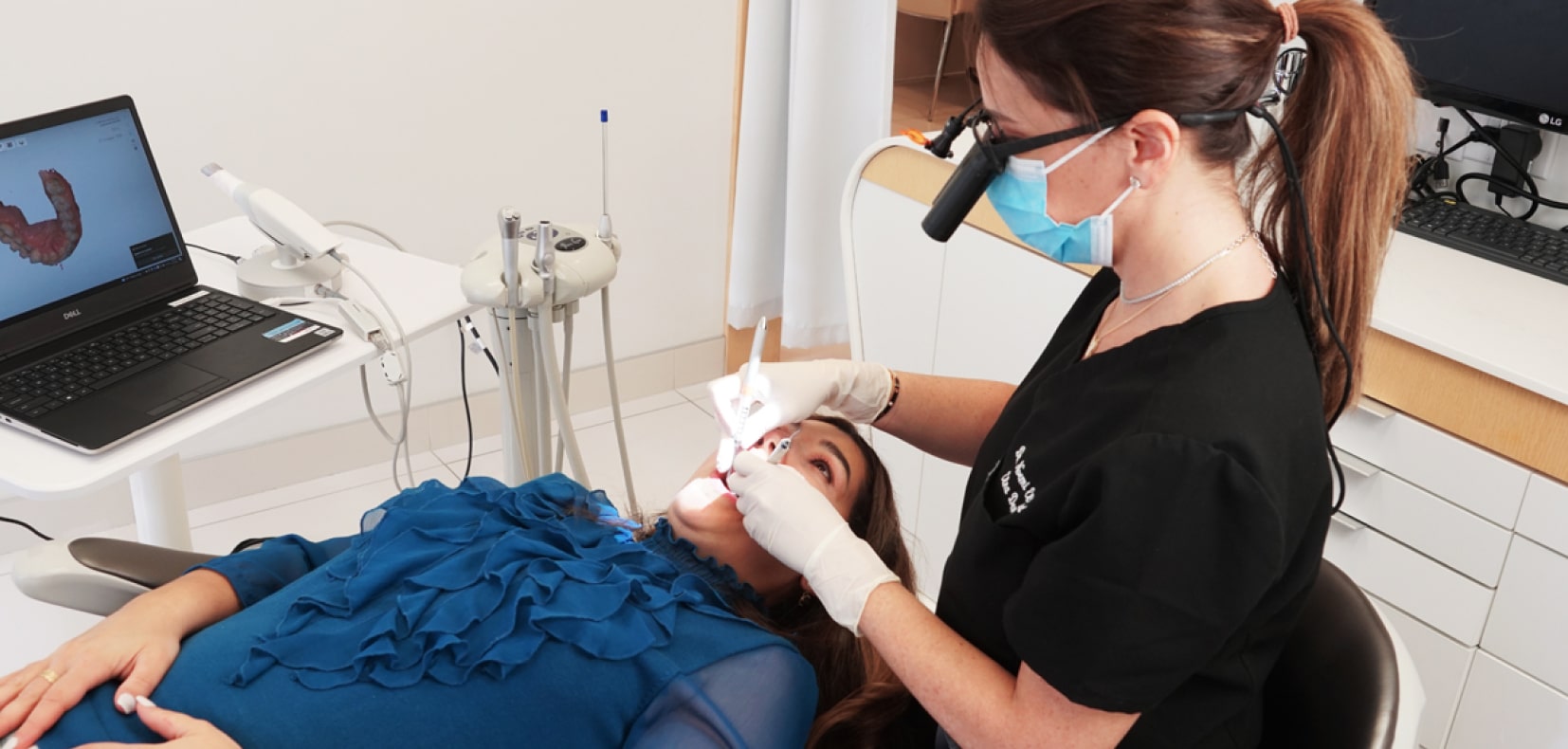
Dentisterie digitale
Nos soins et traitements dentaires
Une équipe multidisciplinaire, de multiples services et traitements dentaires
ELNA Dentaire réunit une équipe de dentistes généralistes et de spécialistes expérimentés de toutes les disciplines.
Les compétences et connaissances de nos praticiens sont complémentaires de sorte à répondre au mieux à la demande de nos patients. Notre équipe s’appuie sur du matériel ultra-moderne de haute technologie pour vous prodiguer les meilleurs soins.
Nous offrons donc un ensemble de services et traitements adaptés pour prendre soin de votre santé bucco-dentaire!

Un panel de soins dentaires pour toute la famille
Dentisterie générale
Dentisterie pédiatrique
- Sensibilisation et apprentissage des bons gestes
- Nettoyage et détartrage
- Scellement de sillons (puits et fissures)
- Traitement des caries
- Extraction des dents
- Sédation consciente
Dentisterie cosmétique
- Facettes dentaires en porcelaine et composite
- Incrustations en porcelaine
- Couronnes dentaires
- Implants dentaires
- Traitement Invisalign
- Design du sourire
Dentisterie préventive
- Bilan de santé
- Examen approfondi
- Radiologie
- Dentisterie opératoire

Service de parodontie
- Examen, nettoyage, détartrage et polissage
- Surfaçage radiculaire
- Chirurgie parodontale et greffe de gencive
- Greffe de gencive
Dentisterie digitale
- Imagerie 3D
- Empreintes numériques
- Planification digitale du sourire
- Simulation du sourire
Votre sourire est notre priorité
Contactez notre équipe pour en savoir plus sur nos services
et planifier une consultation.